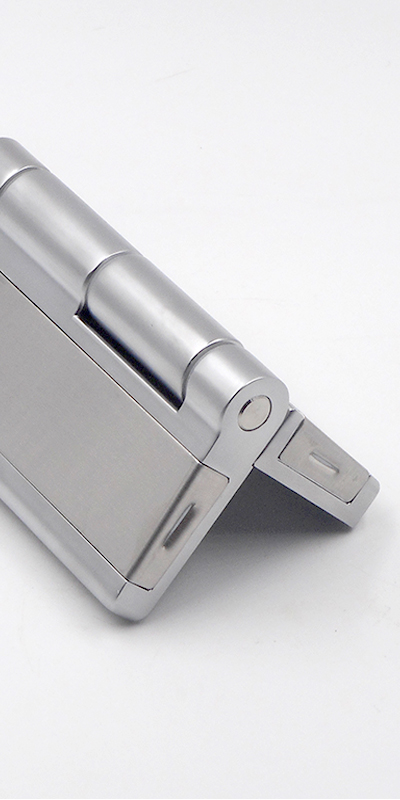
When choosing between zinc alloys and stainless steel, selecting the right material impacts durability, corrosion resistance, and overall cost. Ignoring these differences can lead to poor performance, higher maintenance, and costly replacements. Understanding key distinctions ensures you choose the best material.
Zinc alloys and stainless steel differ in composition, durability, corrosion resistance, cost, and applications. Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and strength, ideal for heavy-duty use, while zinc alloys provide cost-efficiency, lighter weight, and are suitable for applications requiring moderate durability.
Exploring these differences can guide your choice of material for diverse applications.

Composition and Structure
Zinc Alloy consists mainly of zinc, blended with metals like aluminum, copper, or magnesium to enhance strength and casting capabilities. This composition allows zinc alloys to be both malleable and effective for various lightweight applications. For example, zinc alloy is commonly used in Detachable Hinges, where ease of casting and moderate durability are critical.
Stainless Steel, on the other hand, is an iron-based alloy containing chromium (at least 10.5%), often combined with nickel or molybdenum. Chromium forms a protective oxide layer, which is essential in preventing rust and maintaining the alloy’s structural integrity. This makes stainless steel an ideal choice for applications where longevity and resistance to harsh environments are essential.
Corrosion Resistance
Zinc Alloy provides moderate corrosion resistance but can tarnish or corrode over time, especially in humid or acidic environments. It can be coated to improve its durability, although it may still require maintenance in outdoor settings.
Stainless Steel, due to its high chromium content, has excellent corrosion resistance. The oxide layer created by chromium helps it withstand exposure to moisture and corrosive substances, making it highly suitable for applications like Marine Hinges, where consistent contact with water and salt could otherwise lead to rapid degradation.
Durability and Strength
Zinc Alloy has moderate durability and is suitable for applications that do not demand heavy-duty performance. Though versatile and economical, zinc alloy lacks the tensile strength needed for load-bearing applications.
Stainless Steel is known for its strength and robustness, providing excellent durability even under high stress. Its resilience makes it a top choice for industrial, structural, and high-performance applications, especially in products such as Heavy Duty Hinges where reliability under continuous use is essential.

Cost-Effectiveness
Zinc Alloy is typically more cost-effective due to lower material and production costs. This makes it popular for less demanding applications where budget constraints are a primary concern.
Stainless Steel is generally more expensive to produce because of its material composition and durability. However, the higher cost is often justified by its longevity, low maintenance needs, and suitability for heavy-duty applications, offering a better long-term investment in projects requiring high reliability.
Application Suitability
Zinc Alloy finds applications in items requiring intricate casting and lighter weight, such as electronics, consumer goods, and decorative items. Its ability to be easily molded and its lower cost make it ideal for products that require specific shaping and frequent production.
Stainless Steel is favored in applications where strength and resilience against environmental factors are critical, such as construction, industrial components, and marine equipment. Its adaptability makes it a preferred material for high-stakes projects that demand long-term durability.
Visual and Aesthetic Qualities
Zinc Alloy can be polished or plated to enhance its appearance, but it may tarnish or lose its luster over time. Despite this, zinc alloys are often used in decorative applications where cost and appearance are balanced.
Stainless Steel offers natural shine and resists tarnishing, making it visually appealing for premium products. Its ability to maintain its appearance over time makes it ideal for high-end applications that require minimal aesthetic upkeep.

Weight and Density
Zinc Alloy is relatively lightweight, making it advantageous in applications where lower weight is desired. Its density is lower than stainless steel, enabling its use in products where portability or minimal weight is a factor.
Stainless Steel is heavier and denser, which can be beneficial for load-bearing applications. While this weight can be a drawback in certain contexts, it is essential in applications that prioritize stability and structural strength.
Maintenance Requirements
Zinc Alloy typically requires more frequent maintenance due to its susceptibility to tarnishing and corrosion in certain conditions. For outdoor or high-moisture applications, zinc alloy parts may need regular coating or treatment.
Stainless Steel is low maintenance, thanks to its anti-corrosion properties and durability. This makes it ideal for applications where longevity and reduced maintenance costs are priorities, as stainless steel does not require frequent treatments to retain its integrity.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Zinc Alloy is often recyclable, although the recycled material may not always match the quality of the original. Despite this, it is relatively environmentally friendly and can be repurposed effectively.
Stainless Steel is highly recyclable and retains its properties even after recycling, making it a sustainable choice. Its long lifespan and recyclability make it one of the most environmentally conscious options for industrial materials.

Waterproofing and Outdoor Use
Zinc Alloy can withstand moderate exposure to moisture but may not perform as well in continuous outdoor use unless specially coated. The material is best suited for environments that require moderate exposure to water or humidity.
Stainless Steel is naturally resistant to water and outdoor elements, which is why it’s commonly used in external structures or components exposed to harsh weather conditions. Stainless steel is a reliable choice for outdoor applications that require minimal corrosion over time.
Conclusions
Understanding zinc alloy and stainless steel differences is essential to choose materials suited to specific durability, cost, and aesthetic needs.