Hinge gauge is a crucial measurement that determines the strength, durability, and load-bearing capacity of a hinge. It plays a key role in the performance of hinges used in various industrial and mechanical applications. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of hinge gauge, how it affects hinge performance, and why selecting the right gauge is essential for different applications.
Hinge gauge refers to the thickness of the material used to manufacture a hinge. This measurement plays a significant role in determining the hinge’s strength, durability, and its ability to support specific loads. Typically measured in gauge numbers, a lower number corresponds to a thicker material. For example, a 10-gauge hinge will be thicker and stronger than a 16-gauge hinge.
The gauge size you choose for your hinge directly impacts its suitability for the intended application, whether it’s a butt hinge used on doors or a piano hinge for continuous applications. A proper hinge gauge ensures that the hinge can endure the stresses and strains it will face in its working environment.
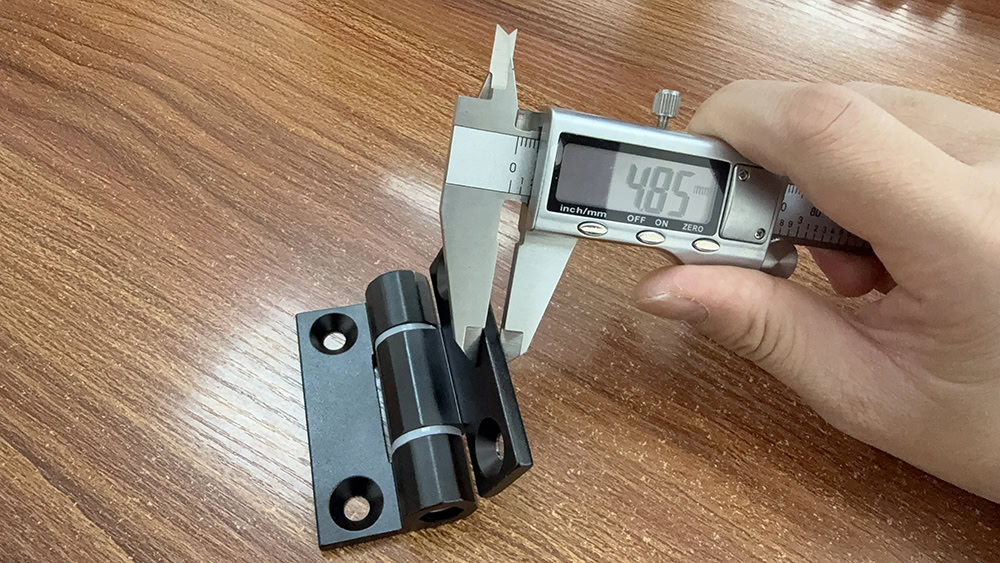

Understanding the Role in Industrial Applications
Industries such as construction, manufacturing, and automotive rely heavily on hinge gauge to ensure their products and equipment are secure, functional, and durable. The gauge determines the hinge’s strength, which is crucial for applications that experience heavy use or need to support substantial weight.
Choosing the correct gauge ensures that marine hinges, for example, can withstand harsh saltwater conditions, or industrial hinge production bases can support heavy doors and machinery without failing. The gauge determines not only the hinge’s durability but also how it performs under stress, making it a vital factor in selecting the right hinge for your needs.
Hinge Gauge and Load-Bearing Capacity
The gauge of a hinge directly affects its load-bearing capacity. A lower gauge number (e.g., 10-gauge) signifies a thicker hinge, which can bear more weight and withstand higher stress. On the other hand, a higher gauge number (e.g., 16-gauge) represents a thinner hinge that is better suited for lighter applications.
When selecting a hinge for heavy-duty equipment, such as weld-on hinges for industrial doors, it is essential to choose a hinge with a lower gauge to ensure that it can carry the required load. In contrast, applications involving lighter doors or smaller equipment may use concealed hinges with a higher gauge, as they need less strength but offer aesthetic appeal.
- Heavy Duty Hinges and Load-Bearing Needs: For doors or equipment that need to support heavy weight, a heavy-duty hinge with a low gauge (e.g., 10 or 12-gauge) is required.
- Light-Duty Hinges: Lighter doors or cabinetry can use thinner gauges, such as 16-gauge, ensuring both cost efficiency and adequate strength.
The Importance of Durability
Durability is one of the most important factors influenced by hinge gauge. Thicker materials (lower gauges) are generally more durable and resistant to wear, making them suitable for high-traffic areas or harsh environments. Conversely, thinner gauges are more prone to wear but may still perform well in low-stress applications.
For example, aluminum hinges with a thicker gauge are ideal for outdoor gates or industrial doors that face constant exposure to the elements. These hinges offer better resistance to fatigue, corrosion, and physical wear compared to those made from thinner materials.
- Fatigue Resistance: A piano hinge made from a thick gauge can resist the repetitive stresses of frequent door openings and closings, ensuring longevity and reduced maintenance.
- Environmental Resistance: In areas such as marine environments, marine hinges must endure harsh saltwater conditions, which makes a thicker, more durable hinge gauge essential.
Cost Efficiency vs. Performance
When considering hinge gauge, there is often a trade-off between cost and performance. Thicker gauges tend to be more expensive but provide superior strength, durability, and long-term value. Conversely, lighter gauges reduce initial costs but may not offer the same lifespan or resistance to wear.
In commercial or industrial settings where longevity and heavy usage are expected. Investing in a heavy-duty hinge with a thicker gauge can reduce the need for frequent replacements, ultimately saving money. However, for light-duty or aesthetic applications, like those using aluminum hinges for cabinetry, thinner gauges may be a more cost-effective solution.
- Cost-Effective Choices: For applications where budget is a primary concern, detachable hinges made from thinner materials are often selected.
- Long-Term Value: For heavy industrial use, investing in hinges with a thicker gauge, such as cold storage room hinges or climatic test chamber hinges, ensures that the hinges will last longer and require fewer replacements.

Selecting the Right Hinge Gauge for Specific Applications
Selecting the correct hinge gauge is vital for ensuring that the hinge can perform its intended function without fail. The gauge influences how the hinge supports weight, endures stress, and withstands environmental factors. Therefore, it is essential to carefully evaluate the needs of your specific project before choosing a hinge.
For instance, in industrial applications, it’s crucial to choose a weld-on hinge with the right gauge to ensure the hinge can withstand the heavy loads and constant motion. In contrast, for decorative or lighter-duty applications, a special hinge with a higher gauge may be sufficient.
- Load and Stress Considerations: For heavy-duty doors, trailer door hinges or marine hinges may require a lower gauge to ensure adequate support.
- Environmental Factors: In environments with extreme conditions, such as cold storage rooms, a thicker gauge helps protect the hinge from wear caused by frequent use and harsh temperatures.
Conclusion
The hinge gauge plays a pivotal role in ensuring the durability, load-bearing capacity. And long-term performance of hinges across various applications. By selecting the right gauge, you can optimize the functionality of hinges used in doors, machinery, and other equipment, ensuring they meet the demands of your specific use case.
Whether you’re choosing butt hinges, industrial hinge production bases, or marine hinges. Understanding hinge gauge is essential for making informed, cost-effective decisions.